- Download kerio VPN client for Mac OS X. To setup Kerio VPN client on Mac, First Download Kerio VPN Client for Mac from the link below: Download Kerio VPN client For Mac(version 8.0.0). Connect to Kerio VPN server. Now lunch Kerio Vpn you’ve just installed inside the System Preference.
- VPN-X:Java/ Cross-platform P2P/SSL/TLS VPN solution.Now the VPN support windows 2000/XP/2003/Vista, linux (x86,x8664b, loongson 2E/F-Mips),Mac OS X (Tiger,Leopard.
The last step in this process is to set up the VPN service on a client computer and then connect to your server. The Server app makes iOS and Mac configuration easy, all you need to do is click the.
Export macOS Server DataWe’re not going to import this, as it only takes a few seconds to configure new settings. Additionally, if you have outstanding services built on macOS Server, you might be able to pull this off without touching client systems. First, let’s grab which protocols are enabled, running the following from Terminal:
sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:com.apple.ppp.pptp:enabled
sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:com.apple.ppp.l2tp:enabled
sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:com.apple.ppp.pptp:IPv4:DestAddressRanges
sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:com.apple.ppp.pptp:DNS:OfferedServerAddresses:_array_index
sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:com.apple.ppp.l2tp:DNS:OfferedServerAddresses:_array_index
sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:com.apple.ppp.l2tp:L2TP:IPSecSharedSecretValue
 Once we have all of this information, we can configure the new server using the same settings. At this point, you can decide whether you want to dismantle the old server and setup a new one on the same IP address, or whether you’d rather just change your port forwards on your router/firewall.
Once we have all of this information, we can configure the new server using the same settings. At this point, you can decide whether you want to dismantle the old server and setup a new one on the same IP address, or whether you’d rather just change your port forwards on your router/firewall.Ports
Before we configure any VPN services, let’s talk about ports. The following ports need to be opened per The Official iVPN Help Docs (these are likely already open if you’re using a macOS Server to provide VPN services):
- PPTP: TCP port 1723
- L2TP: UDP ports 1701, 4500 and 500
- Enable VPN pass-through on the firewall of the server and client if needed
openvpn
There are a number of ways to get a VPN Server installed on macOS. One would be to install openvpn:
sudo port -v install openvpn2OpenVPN has a lot of sweet options, which you can read about at openvpn.net.
 SoftEther
SoftEtherOne of the other tools Apple mentioned is SoftEther. I decided not to cover it here because it uses Wine. And I’m not a fan of Wine.
Or Use iVPN
That will require some work to get dependencies and some working with files and network settings. Another option would be to install iVPN from here, on the Mac App Store. You can install it manually as well, and if you do, you’ll need to pay separately through PayPal, which is what we’ll cover here.
Once installed, if you purchased the license separately, use the Enter Manually button to provide it.
At the Registration screen, make sure the name, email, and serial are entered exactly as you see them in the email you received.
At the Thank You screen, click OK.
At the EULA screen, click Accept assuming you accept the license agreement.
Configure iVPN
At the main screen, you’ll have a few options, which we’ll unpack here:
- Use Directory Server: Allows you to use an LDAP or Active Directory connection to provide username and passwords to the service.
- Use custom accounts: Allows you to manually enter accounts to provide username and passwords for clients to connect to the
- Shared Secret: The secret, or a second factor used with L2TP connection.
- Allow 40-bit encryption keys: Allows clients to use lower levels of encryption. Let’s not do this.
- IP Address Range: The beginning and ending IP that will be manually handed out to client computers. When configuring the range, take care not to enter a range of addresses in use by any other DHCP services on your network or you will end up with conflicts.
- Basic DNS: Allows you to configure a primary and second DNS server to send to clients via DHCP when they connect to the VPN interface.
- Advanced DNS: Allows you to configure DNS servers as well as Search Domains.
- Configure Static Routes: Allows you to specify the interface and netmask used to access a given IP.
- Export Configuration Profile: Exports a configuration profile. When imported into a Mac or iOS device, that profile automatically configures the connection to the PPTP or L2TP service you’ve setup.
- VPN Host Name: Used for the configuration profile so a client system can easily find the server w
If you configure Directory Authentication, you’ll get prompted that it might be buggy. Click OK here.
The Directory Authentication screen allows you to choose which directory services to make available to PPTP or L2TP. If the system hasn’t been authenticated to a directory server, do so using the Users & Groups” System Preference pane.
Once you’ve chosen your directory service configuration, if you require a third DNS server, click on Advanced DNS and then enter it, or any necessary search-domains. Click Done when you’re finished.
Click the log button in the upper left-hand side to see the logs for the service. This is super-helpful when you start troubleshooting client connections or if the daemon stops for no good reason (other than the fact that you’re still running a VPN service on macOS Server and so the socket can’t bind to the appropriate network port).
Finally, you can also create a static route. Static routing provides a manually-configured routing entry, rather than information from a dynamic routing traffic, which means you can fix issues where a client can’t access a given IP because it’s using an incorrect network interface to access an IP.
Once everything is configure, let’s enter the publicly accessible IP address or DNS name of the server. Client computers that install the profile will then have their connection to the server automatically configured and will be able to test the connection.
Configure Clients
If you configured the new server exactly as the old one and just forwarded ports to the new host, you might not have to do anything, assuming you’re using the same username and password store (like a directory service) on the back-end. If you didn’t, you can setup new interfaces with a profile. If you pushed out an old profile to configure those, I’d recommend removing it first if any settings need to change. To configure clients, we’ll install the new profile. When you open the profile on a client system (just double-click it to open it), you’ll see the Install dialog box. Here, click on Continue.
How To Set Up A Vpn Server
Because the profile isn’t signed, you’ll then get prompted again (note: you can sign the profile using another tool, like an MDM or Apple Configurator). Click Continue.Then enter the username that will be used to connect to the VPN and click the Install button.
The Profile can then be viewed and manually removed if needed.
Click on the new iVPN entry in the Network System Preference pane. Here, you can enable
Now that it’s easy, let’s click the VPN icon in the menu bar and then click on Connect iVPN to test the connection.
Once clients can connect, you can use the iVPN icon in the menu bar to monitor the status of clients.
Table of contents
- 1.1. Initial configurations (only once at the first time)
- 2.2. Start a VPN connection
- 3.3. Enjoy VPN communication
Here is an instruction how to connect to a VPN Gate Public VPN Relay Server by using L2TP/IPsec VPN Client which is built-in on Mac OS X.
On this instruction, every screen-shots are taken on Mac OS X Mountain Lion. Other versions of Mac OS X are similar to be configured, however there might be minor different on UIs.
These screen-shots are in English version of Mac OS X. If you use other language, you can still configure it easily by referring the following instructions.
Best Vpn For Macbook Free
1. Initial configurations (only once at the first time)
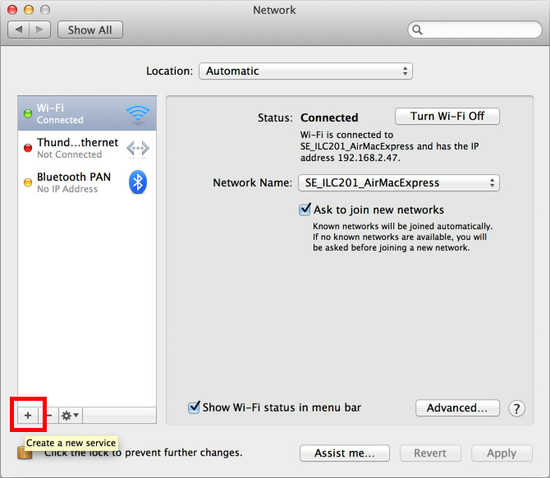
Click the network icon on the top-right side on the Mac screen. Click 'Open Network Preferences...' in the menu.
Click the '+' button on the network configuration screen.
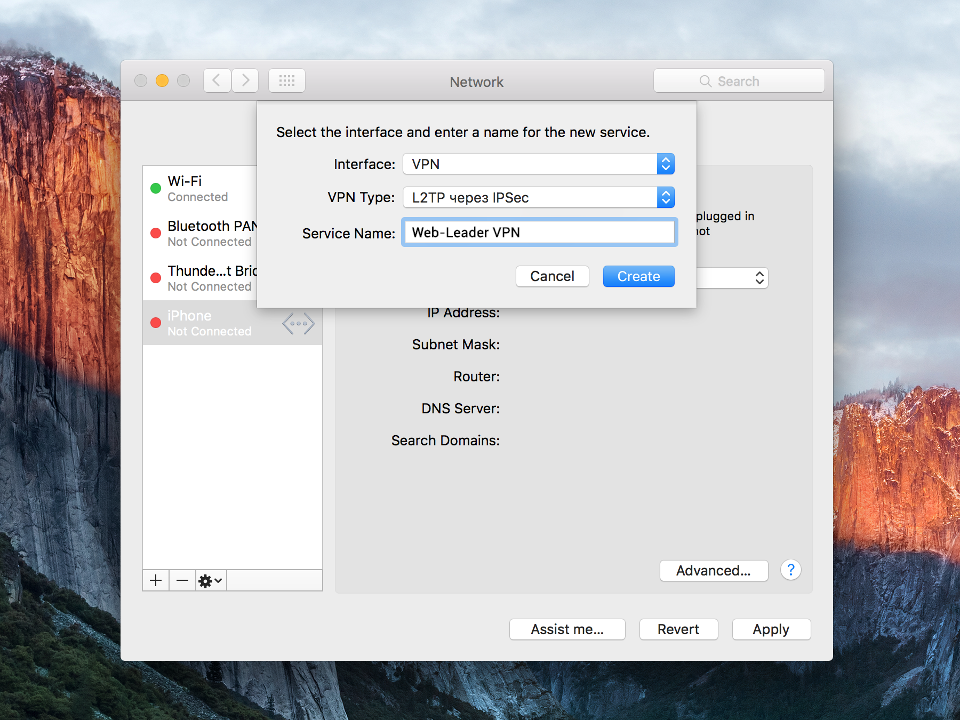
Select 'VPN' as 'Interface' , 'L2TP over IPsec' as 'VPN Type' and click the 'Create' button.
A new L2TP VPN configuration will be created, and the configuration screen will appear.
On this screen, you have to specify either hostname or IP address of the destination SoftEther VPN Server.
After you specified the 'Server Address' , input the user-name on the 'Account Name' field, which is the next to the 'Server Address' field.
Vpn Server For Mac Os Catalina
Next, click the 'Authentication Settings...' button.
The authentication screen will appear. Input your password in the 'Password' field. Specify the pre-shared key also on the 'Shared Secret' field. After you input them, click the 'OK' button.
After return to the previous screen, check the 'Show VPN status in menu bar' and click the 'Advanced...' button.
The advanced settings will be appeared. Check the 'Send all traffic over VPN connection' and click the 'OK' button.
On the VPN connection settings screen, click the 'Connect' button to start the VPN connection.
2. Start a VPN connection
You can start a new VPN connection by clicking the 'Connect' button at any time. You can also initiate a VPN connection by clicking the VPN icon on the menu bar.
After the VPN connection will be established, the VPN connection setting screen will become as below as the 'Status' will be 'Connected' . Your private IP address on the VPN, and connect duration time will be displayed on the screen.
Vpn Server For Mac Os High Sierra
3. Enjoy VPN communication
Vpn Server For Macos
While VPN is established, all communications will be relayed via the VPN Server. You can access to any local servers and workstation on the destination network.
